Understanding Headless Vs. Composable Commerce
The eCommerce landscape has seen big changes, moving from traditional setups to flexible headless commerce and now to cutting-edge composable commerce. This guide takes you through this journey and explains why composable commerce is now a top choice for businesses seeking great flexibility and customization.
Learn about the differences and find out how composable commerce could help your business stand out in today's fast-moving digital market.
What is Headless eCommerce?
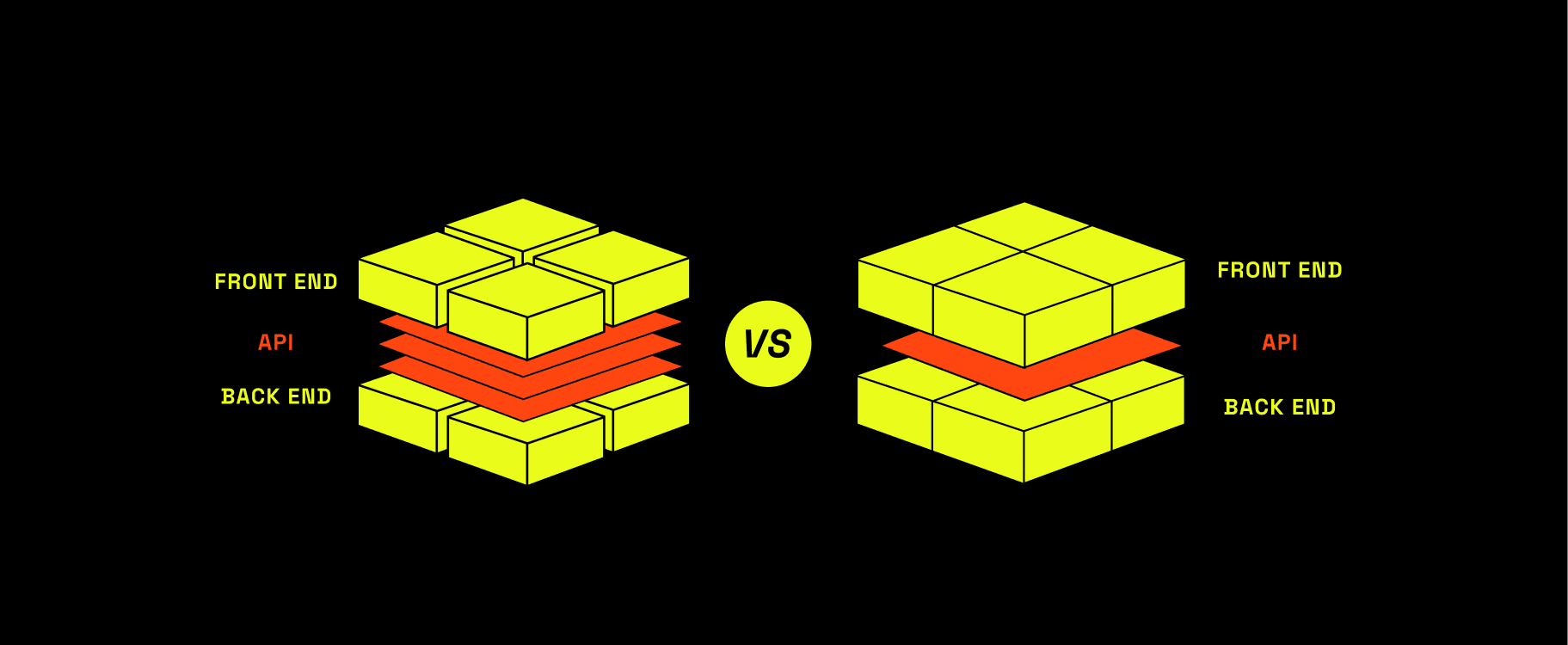
Headless commerce is an architecture that separates the frontend user interface from the backend eCommerce operations.
Headless commerce architecture decouples the online store's frontend—where customers browse and shop—from the backend, which manages data and processes like product inventory, orders, and customer information. Through APIs, the frontend and backend communicate independently, enabling updates or changes to the store's design, features, or technology without overhauling the entire system.
This setup not only enhances flexibility in presenting the store to customers but also allows for rapid adaptation to market trends or customer preferences.
Moreover, headless commerce supports personalized shopping experiences across different channels, such as mobile apps or social media, by tailoring the frontend for each platform while maintaining a consistent backend operation.
What is Composable eCommerce?
Composable commerce is an approach where businesses can select and integrate many different commerce components, like inventory management, payment processing, or customer interface, via APIs. This modular setup allows for a highly tailored ecommerce system that can easily adapt and scale to meet different business needs and customer demands.
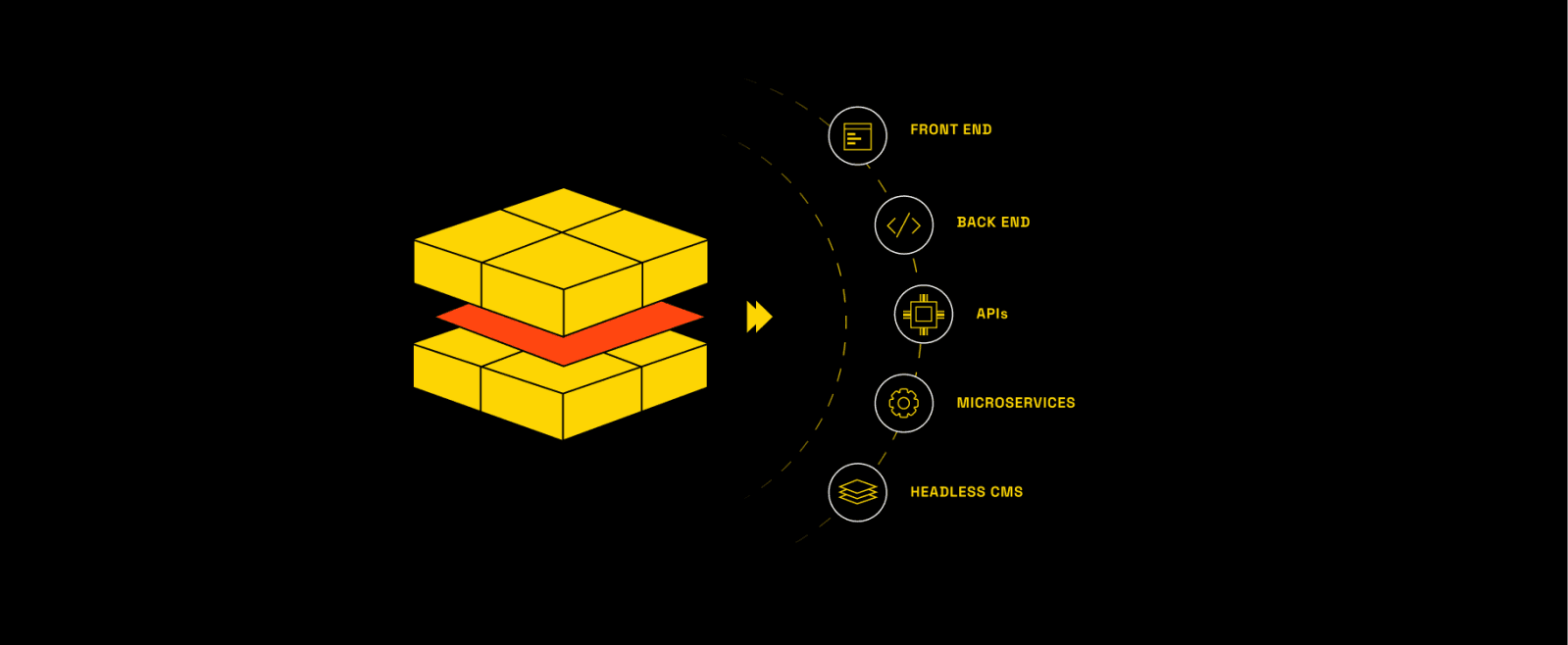
Taking the concept of headless commerce further, composable commerce architecture breaks down the backend into smaller, independent services or components. Unlike headless commerce, which primarily decouples the frontend from the backend, composable commerce offers even greater modularity by segmenting the backend into microservices. This segmentation allows businesses to assemble a custom ecommerce platform by selecting the best components for their specific needs, ensuring each function, from payments to shipping, is optimally addressed.
The communication between these components and the frontend, facilitated through APIs, enables a level of flexibility and customization unparalleled in traditional ecommerce setups.
Composable commerce's granular approach allows for a more precise tailoring of the ecommerce experience to a business's unique workflows and customer expectations.
Headless Vs. Composable Commerce: Market Share
The headless commerce market is expected to grow really big, reaching about $3,811.3 million by 2030. It's growing super fast, too, at a rate of 22.5% every year from 2023 to 2030. This means a lot more companies are starting to use headless commerce because it's flexible and lets them create better online shopping experiences.
The composable applications market was worth $5.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach about $27.71 billion by 2033, a growth rate of 17.60% each year.
North America is leading the charge, holding almost half the market share 2023. It's a hot spot for composable apps because of its strong economy and love for new tech. In the U.S. alone, the market for composable apps was $1.81 billion in 2023, and it's predicted to hit around $9.19 billion by 2033.
Headless vs. Composable eCommerce: Cost Analysis
In composable commerce, the cost factors are closely tied to its microservice architecture. This setup allows businesses to tailor their eCommerce system with specific functionalities they need.
While customizing and integrating these microservices can require a significant investment in development and maintenance, it's important to note that this architecture offers the advantage of avoiding vendor lock-in and enabling businesses to choose the best solutions for each function. Yes, evaluating, integrating, and managing these services can introduce additional costs, including licensing and support fees. The ability to scale services independently may lead to increased infrastructure and operational management expenses.
However, the flexibility and future-proofing offered by composable commerce could lead to significant cost savings in the long run, as it allows for easier adaptation and updates to the eCommerce platform.
Headless commerce focuses on front-end flexibility, facilitating customer experience innovations with minimal backend changes, potentially reducing costs related to new designs or interfaces. However, its API-dependent model for backend integration could raise costs associated with API development and maintenance. It's vital to consider the total cost of ownership, including development, support, hosting, and maintenance, to fully understand the financial impact.
When comparing both architectures, this question becomes important -
- Do you require the flexibility to innovate on the front end rapidly, or is a fully customizable system across all operations more critical?
- Carefully selecting vendors and technology partners can help balance cost-effectiveness with the required expertise and reliability. Additionally, while composable commerce might offer a quicker time-to-market due to its modular nature, initial setup and maintenance costs should not be overlooked.
- Ultimately, the flexibility and future-proofing offered by composable commerce could lead to cost savings in the long run, as it allows for easier adaptation and updates to the eCommerce platform.
Headless Vs. Composable eCommerce: Top Challenges
Headless Commerce Challenges:
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the frontend with various backend services and APIs can be complex and time-consuming, requiring deep technical expertise.
- Learning Curve: Teams may face a steep learning curve with the frontend technologies and headless CMS platforms, especially if they are accustomed to traditional, monolithic systems.
- Management Overhead: While the frontend can be updated more flexibly, managing and maintaining separate systems for the frontend and backend increases operational overhead.
Composable Commerce Challenges:
- System Cohesion: Ensuring seamless operation among independently developed components can be challenging, as each component may have its own set of APIs, data models, and update cycles.
- Integration Overhead: While composable commerce allows for best-of-breed solutions, integrating these disparate systems and ensuring they work harmoniously together requires significant effort and expertise.
- Complexity in Scalability: Although composable commerce is inherently scalable, the complexity of managing and scaling multiple components, especially in a rapidly evolving market, can be daunting.
The Verdict:
Both headless and composable commerce introduce integration challenges and a learning curve with new technologies. While headless involves managing two distinct systems, composable commerce's complexity lies in coordinating numerous components. Although composable commerce addresses scalability through its modular nature, this very flexibility adds complexity due to the diverse scalability needs of each component.
Benefits of Headless Commerce
- Enhanced Performance: Separating front and back ends boosts site speed and user experience, notably improving page load times.
- Customized Branding: Offers limitless customization, enabling unique brand presentations and customer experiences beyond standard templates.
- Agile Innovation: Its decoupled structure permits rapid experimentation and adoption of new frontend technologies, independent of backend constraints.
- Easier Integrations: Simplifies connecting with third-party services, augmenting site functionality, including payment systems.
- Higher Conversion Rates: The ability to tailor user experiences precisely can significantly increase customer engagement and conversions.
- Omnichannel Support: Facilitates a unified and quality shopping experience across all customer touchpoints, from web to mobile.
Benefits of Composable Commerce
- Modular Flexibility: Enables precise customization of the eCommerce platform by choosing and integrating the best components for specific functions.
- Rapid Adaptability: Facilitates swift adjustments to market trends or technology shifts, allowing for easy updates or swaps of components.
- Cost Efficiency: Offers cost savings by allowing businesses to invest only in essential components, reducing waste associated with all-in-one systems.
- Enhanced Scalability: Supports business growth seamlessly, with the ability to add or update components without system-wide disruptions.
- Future-proofing: Keeps eCommerce platforms competitive and up-to-date, accommodating ongoing changes in the digital market.
- Streamlined Operations: Improves operational efficiency by utilizing top-tier solutions for different eCommerce processes, enhancing overall performance.
Conclusion
You should consider headless commerce if their priority is to enhance the customer-facing side of their online store with custom, cutting-edge frontend experiences, and they have the technical resources to handle the separation of frontend and backend. Composable commerce is the better choice for businesses looking for total flexibility across their entire technology stack, willing to invest in integrating and managing multiple best-of-breed solutions to tailor every aspect of their operations.
Essentially, the decision hinges on the specific needs for customization, the level of control desired over the eCommerce architecture, and the business's capacity to manage the complexity of their chosen solution.
FAQs
Is MACH architecture and composable commerce the same?
No, they’re not the same, as well. MACH architecture is just one way to implement composable commerce through its four main principles: microservices, API-first, cloud-native, and headless.